The NWEA MAP (Measures of Academic Progress) test is a widely used assessment tool designed to measure student growth and proficiency in core academic areas. It is administered to students in grades K-12 and provides valuable insights into their learning progress. In this blog post, we’ll explore what the NWEA MAP test is, how it works, and how to interpret NWEA MAP test scores to support student success.
What is the NWEA MAP Test?
The NWEA MAP test is a computer-adaptive assessment created by the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA). Unlike traditional standardized tests, the MAP test adapts to each student’s performance in real time. This means that the difficulty of the questions adjusts based on whether a student answers correctly or incorrectly, providing a more accurate measure of their academic abilities.
The test covers three main subject areas:
- Mathematics: Assesses problem-solving, computation, and mathematical reasoning.
- Reading: Evaluates reading comprehension, vocabulary, and language usage.
- Science: Measures understanding of scientific concepts, reasoning, and inquiry skills (though not all schools administer the science portion).
The MAP test is typically administered two to three times per school year (fall, winter, and spring), allowing educators to track student growth over time.
How Does the NWEA MAP Test Work?
The adaptive nature of the NWEA MAP test is one of its key features. Here’s how it works:
- Starting Point: Each student begins the test with a question that matches their map scores by grade level 2024.
- Adaptive Questions: If a student answers a question correctly, the next question becomes more challenging. If they answer incorrectly, the next question is easier.
- Personalized Assessment: This process continues throughout the test, ensuring that each student’s assessment is tailored to their individual skill level.
- Immediate Results: After completing the test, educators and parents receive detailed reports that highlight the student’s strengths and areas for improvement.
This adaptive approach ensures that the test is neither too easy nor too difficult, providing a more accurate picture of a student’s academic abilities.
Understanding NWEA MAP Test Scores
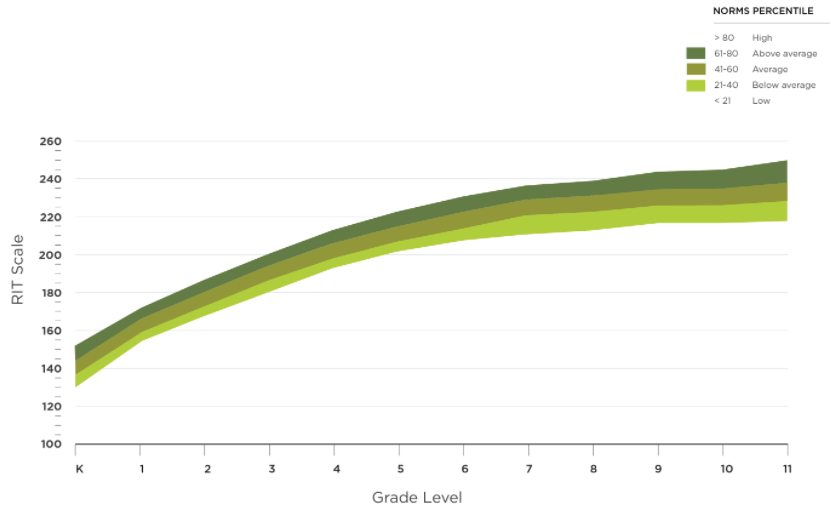
NWEA MAP test scores are reported using a unique scoring system called the RIT (Rasch Unit) scale. The RIT scale is an equal-interval scale, similar to a ruler, that measures student achievement and growth over time. Here’s a breakdown of the key components of NWEA MAP test scores:
RIT Scores
The RIT score is the most important number on a student’s MAP test report. It represents their academic achievement in a specific subject area. Key points to know about RIT scores include:
- Range: RIT scores typically range from 140 to 300, depending on the student’s grade level and subject.
- Growth Over Time: Since the MAP test is administered multiple times per year, educators can track a student’s RIT score growth from one testing period to the next.
- Norms: NWEA provides national norms, which allow educators to compare a student’s RIT score to the average performance of students in the same grade across the country.
Percentile Rank
The percentile rank indicates how a student’s RIT score compares to other students in the same grade and subject. For example, if a student has a percentile rank of 75, it means they scored higher than 75% of their peers.
Growth Projections
NWEA MAP test reports also include growth projections, which estimate how much a student is expected to grow by the next testing period. These projections help educators set realistic goals and identify students who may need additional support.
Lexile® Measures (Reading)
For the reading portion of the MAP test, students receive a Lexile measure, which helps match them with books and reading materials that align with their reading level. This is a valuable tool for encouraging independent reading and improving literacy skills.
How to Use NWEA MAP Test Scores
NWEA MAP test scores are more than just numbers—they provide actionable insights that can guide instruction and support student learning. Here’s how educators and parents can use these scores effectively:
For Educators
- Differentiated Instruction: Use RIT scores to identify students’ strengths and weaknesses, and tailor instruction to meet their individual needs.
- Monitor Progress: Track student growth over time to ensure they are making adequate progress toward academic goals.
- Intervention Strategies: Identify students who may need additional support and provide targeted interventions to help them catch up.
For Parents
- Understand Your Child’s Performance: Review the RIT scores and percentile ranks to understand how your child is performing compared to their peers.
- Support Learning at Home: Use the Lexile measure to find books that match your child’s reading level and encourage a love of reading.
- Communicate with Teachers: Discuss your child’s MAP test results with their teacher to better understand their academic progress and how you can support their learning at home.
Conclusion
The NWEA MAP test is a powerful tool for measuring student growth and academic achievement. Its adaptive design ensures that each student’s assessment is personalized, while the RIT scale provides a clear and consistent way to track progress over time. By understanding NWEA MAP test scores, educators and parents can work together to support student success and foster a love of learning. Whether you’re a teacher, parent, or student, the insights provided by the MAP test can help guide instruction, set goals, and celebrate academic growth.